Hello friends!
इस पोस्ट में Contiguous & Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation in Hindi के बारे में पूरी जानकारी आसान हिंदी भाषा में समझाई गई है।
यदि आप इस टॉपिक के बारे में जानना चाहते हैं, तो इस पोस्ट को पूरा जरूर पढ़ें।
Table of Contents
परिचय (Introduction)
Operating System में Memory Allocation का मतलब है processes को main memory (RAM) में जगह देना। Memory allocation के दो प्रमुख तरीके होते हैं – Contiguous Memory Allocation और Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation। दोनों का अपना use-case, फायदे और limitations होते हैं।
Contiguous Memory Allocation क्या है?
Contiguous Memory Allocation वह technique है जिसमें एक process को memory में continuous (लगातार) blocks दिए जाते हैं। Process का पूरा address space एक ही जगह पर store होता है।
Example:
अगर process को 100KB memory चाहिए, तो उसे RAM में 100KB की continuous free space मिलनी चाहिए।
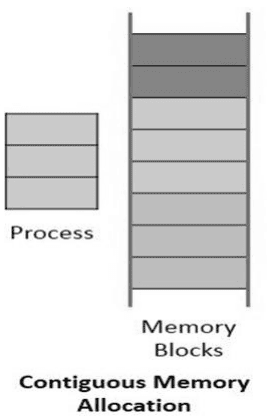
Contiguous Memory Allocation के प्रकार
1. Fixed Partitioning
- Memory को fixed size partitions में divide किया जाता है
- Internal fragmentation की समस्या
2. Variable Partitioning
- Process size के अनुसार memory allocate
- External fragmentation की समस्या
Contiguous Memory Allocation के फायदे
- Simple implementation
- Fast access time
- Easy address calculation
नुकसान
- External/Internal fragmentation
- Large process के लिए suitable नहीं
- Poor memory utilization
Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation क्या है?
Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation में process के memory blocks RAM में अलग-अलग जगहों पर store हो सकते हैं। Continuous space की आवश्यकता नहीं होती।
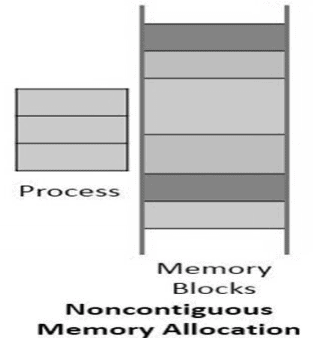
Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation के प्रकार
1. Paging
- Memory को fixed-size pages और frames में divide किया जाता है
- External fragmentation नहीं होती
2. Segmentation
- Logical segments (code, data, stack)
- User view के करीब
3. Paging with Segmentation
- Paging + Segmentation का combination
Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation के फायदे
- Better memory utilization
- Fragmentation कम
- Large programs के लिए suitable
नुकसान
- Complex implementation
- Address translation overhead
- Hardware support जरूरी
Contiguous vs Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation
| आधार | Contiguous | Non-Contiguous |
|---|---|---|
| Memory blocks | Continuous | Non-continuous |
| Fragmentation | High | Low |
| Implementation | Simple | Complex |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Example | Fixed partition | Paging |
Real-Life Example
- Contiguous: Cinema hall में एक group को साथ की seats
- Non-Contiguous: Train में अलग-अलग bogies में seats
FAQs – Memory Allocation
Contiguous memory allocation क्या है?
Continuous blocks में memory देना।
Non-contiguous memory allocation क्यों बेहतर है?
Memory utilization बेहतर होने के कारण।
निष्कर्ष (Conclusion)
Contiguous और Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation दोनों Operating System के महत्वपूर्ण concepts हैं। Modern OS ज्यादातर Non-Contiguous methods (Paging/Segmentation) का उपयोग करते हैं क्योंकि ये ज्यादा efficient और scalable होते हैं।
👉 Next Topic: Directory Structure in Hindi – डायरेक्टरी स्ट्रक्चर क्या है?
